store at low temperature
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year

3-Hydroxybutyric acid (Butanoic acid) (or beta-hydroxybutyrate) is a ketone body. Like the other ketone bodies (acetoacetate and acetone), levels of 3-hydroxybutyrate in blood and urine are raised in ketosis. In humans, 3-hydroxybutyrate is synthesized in the liver from acetyl-CoA and can be used as an energy source by the brain when blood glucose is low. Blood levels of 3-hydroxybutyric acid levels may be monitored in diabetic patients to look for diabetic ketoacidosis. Persistent mild hyperketonemia is a common finding in newborns. Ketone bodies serve as an indispensable source of energy for extrahepatic tissues, especially the brain and lung of developing mammals. Another important function of ketone bodies is to provide acetoacetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA for the synthesis of cholesterol, fatty acids, and complex lipids. During the early postnatal period, acetoacetate (AcAc) and beta-hydroxybutyrate are preferred over glucose as substrates for synthesis of phospholipids and sphingolipids in accord with requirements for brain growth and myelination. Thus, during the first 2 weeks of postnatal development, when the accumulation of cholesterol and phospholipids accelerates, the proportion of ketone bodies incorporated into these lipids increases. On the other hand, an increased proportion of ketone bodies is utilized for cerebroside synthesis during the period of active myelination. In the lung, AcAc serves better than glucose as a precursor for the synthesis of lung phospholipids. The synthesized lipids, particularly dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, are incorporated into surfactant, and thus have a potential role in supplying adequate surfactant lipids to maintain lung function during the early days of life (PMID: 3884391 ). 3-Hydroxybutyric acid is found to be associated with fumarase deficiency and medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, which are inborn errors of metabolism.
| Pack Size | Availability | Price/USD | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | In stock | $ 41.00 |




| Description | 3-Hydroxybutyric acid (Butanoic acid) (or beta-hydroxybutyrate) is a ketone body. Like the other ketone bodies (acetoacetate and acetone), levels of 3-hydroxybutyrate in blood and urine are raised in ketosis. In humans, 3-hydroxybutyrate is synthesized in the liver from acetyl-CoA and can be used as an energy source by the brain when blood glucose is low. Blood levels of 3-hydroxybutyric acid levels may be monitored in diabetic patients to look for diabetic ketoacidosis. Persistent mild hyperketonemia is a common finding in newborns. Ketone bodies serve as an indispensable source of energy for extrahepatic tissues, especially the brain and lung of developing mammals. Another important function of ketone bodies is to provide acetoacetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA for the synthesis of cholesterol, fatty acids, and complex lipids. During the early postnatal period, acetoacetate (AcAc) and beta-hydroxybutyrate are preferred over glucose as substrates for synthesis of phospholipids and sphingolipids in accord with requirements for brain growth and myelination. Thus, during the first 2 weeks of postnatal development, when the accumulation of cholesterol and phospholipids accelerates, the proportion of ketone bodies incorporated into these lipids increases. On the other hand, an increased proportion of ketone bodies is utilized for cerebroside synthesis during the period of active myelination. In the lung, AcAc serves better than glucose as a precursor for the synthesis of lung phospholipids. The synthesized lipids, particularly dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, are incorporated into surfactant, and thus have a potential role in supplying adequate surfactant lipids to maintain lung function during the early days of life (PMID: 3884391 ). 3-Hydroxybutyric acid is found to be associated with fumarase deficiency and medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, which are inborn errors of metabolism. |
| Synonyms | Butanoic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 104.1 |
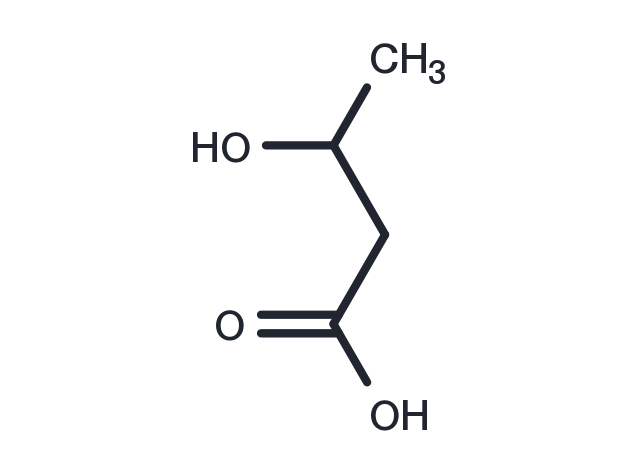
| Formula | C4H8O3 |
| CAS No. | 300-85-6 |
store at low temperature
Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year
H2O: 200mg/mL(1.92 M)
DMSO: 10 mM
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More
bottom
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc.
3-Hydroxybutyric acid 300-85-6 Metabolism Endogenous Metabolite inhibit Inhibitor Butanoic acid diabetes β-Hydroxybutyric acid 3Hydroxybutyric acid membrane metabolite lipids 3 Hydroxybutyric acid type inhibitor
